Meet Dr. Jon Gaffney – Hair Restoration Surgeon
Dr. Jon Gaffney, M.D., is a highly experienced hair restoration specialist with over 30 years of expertise and 16,000+ successful hair transplants performed. A board-certified plastic surgeon, he has trained at top institutions, served in Operation Desert Storm, and held leadership roles at Bosley Medical Group and Hair Club for Men. Currently practicing at Advanced Hair Restoration, Dr. Gaffney combines surgical precision with advanced techniques to deliver natural, lasting results.
Professional Affiliations:
- American Society of Plastic Surgeons
- International Society of Hair Restoration Surgery (Associate Member)
- Fellow of the American College of Surgeons
- Diplomate, American Board of Plastic Surgeons
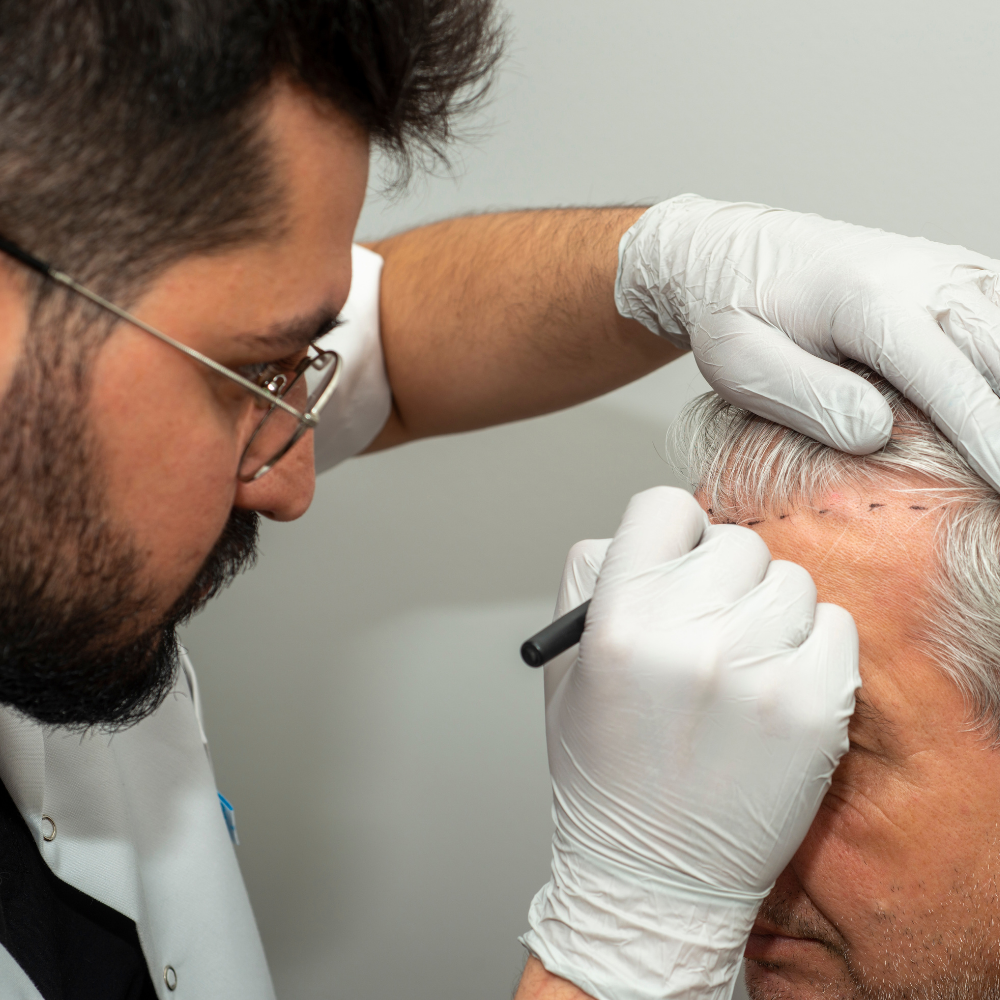
How Hair Transplant Works
Transplanted follicles maintain their original growth characteristics, ensuring continuous hair growth in the recipient area. Surgeons meticulously place each follicle to align with your natural hair pattern, achieving a seamless appearance.
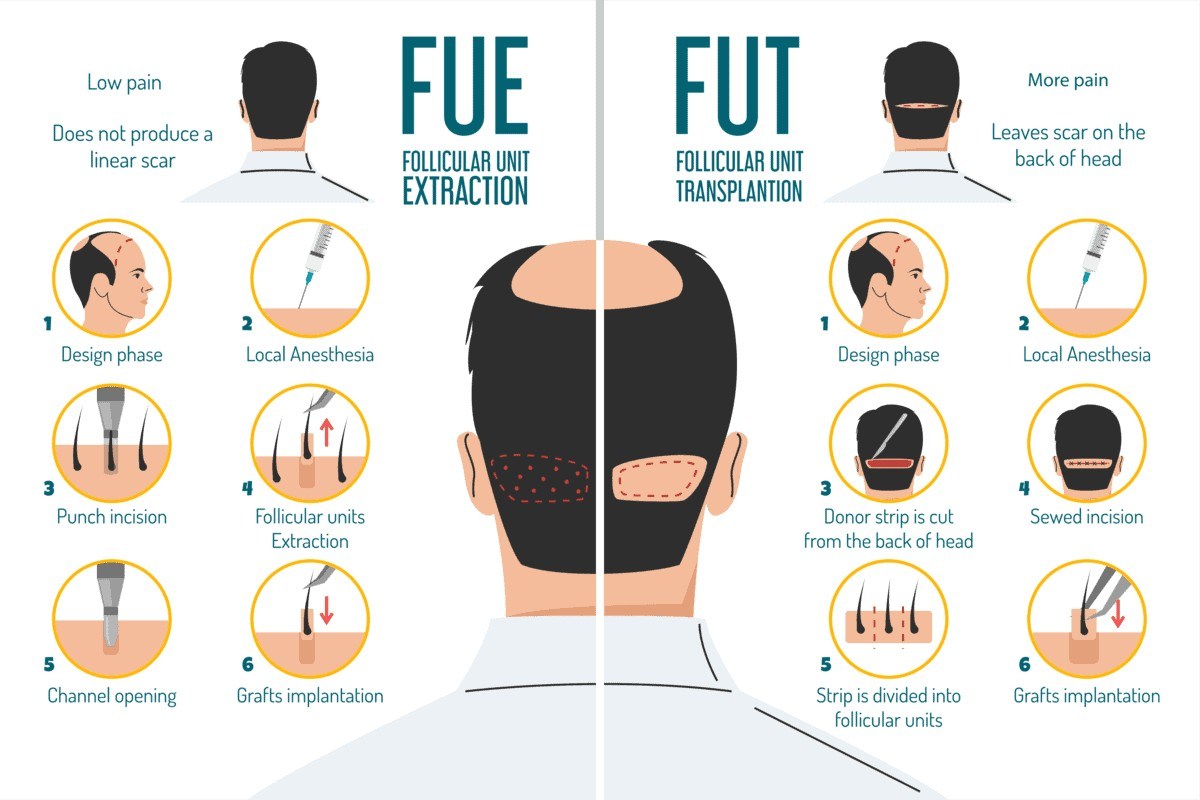
Two Main Types of Hair Transplant Techniques:
1. FUE (Follicular Unit Extraction)
This advanced, minimally invasive technique involves extracting individual hair follicles directly from the donor area, typically the back or sides of the scalp, and transplanting them to thinning or balding areas. Since no large incision is made, it leaves no linear scar, resulting in a more natural-looking outcome with faster healing and minimal discomfort.
2. FUT (Follicular Unit Transplantation):
Also known as the strip method, this traditional hair restoration technique involves surgically removing a strip of scalp from the donor area, from which follicular units are carefully extracted and implanted into the recipient site. While highly effective for restoring hair density, it may leave a linear scar at the donor site and typically requires a slightly longer recovery period compared to FUE.
Procedure Overview
Conducted as an outpatient procedure under local anesthesia, hair transplantation involves harvesting donor hair and transplanting it to target areas. Recovery is swift, with many resuming regular activities within days.
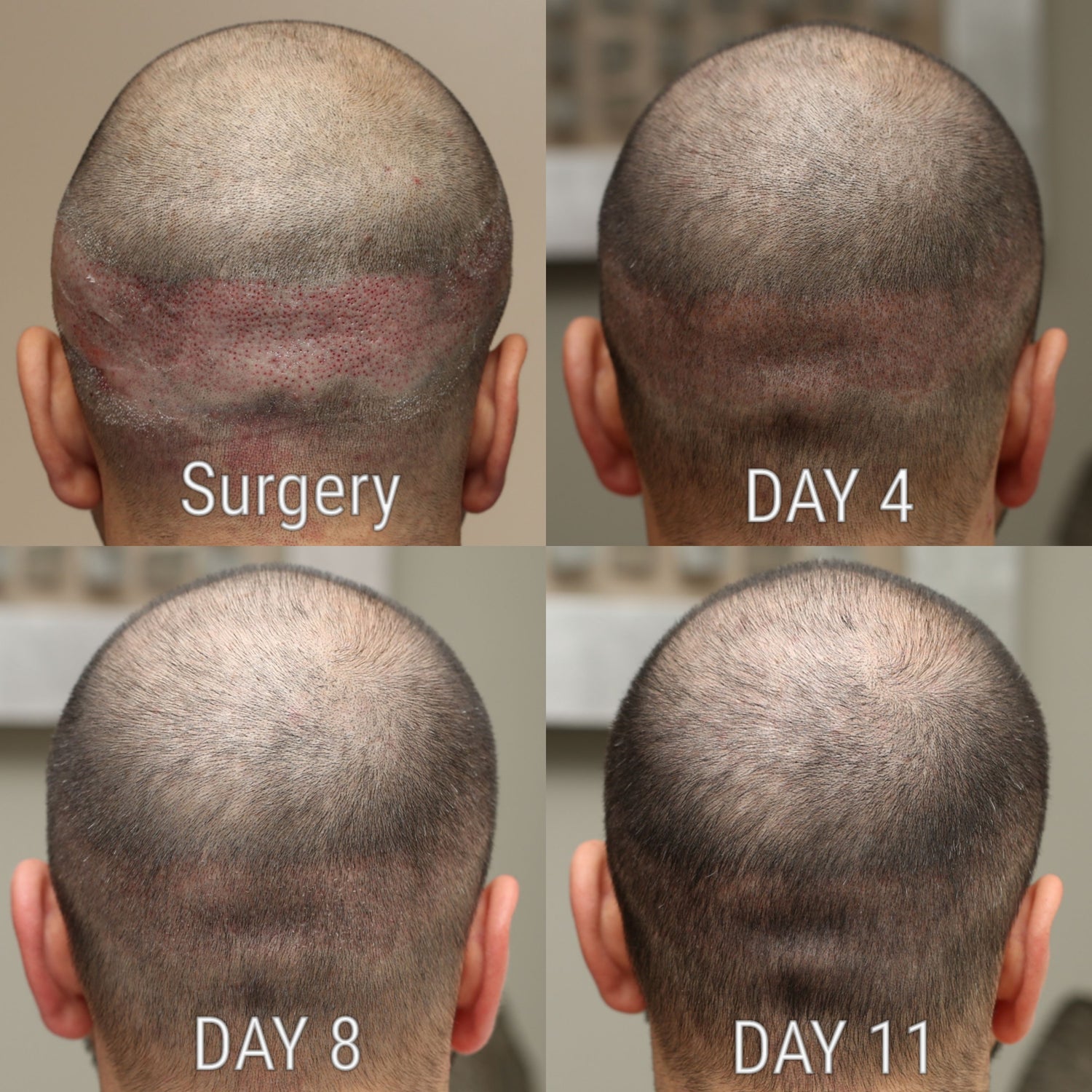
Recovery Timeline
Conducted as an outpatient procedure under local anesthesia, hair transplantation involves harvesting donor hair and transplanting it to target areas. Recovery is swift, with many resuming regular activities within days.
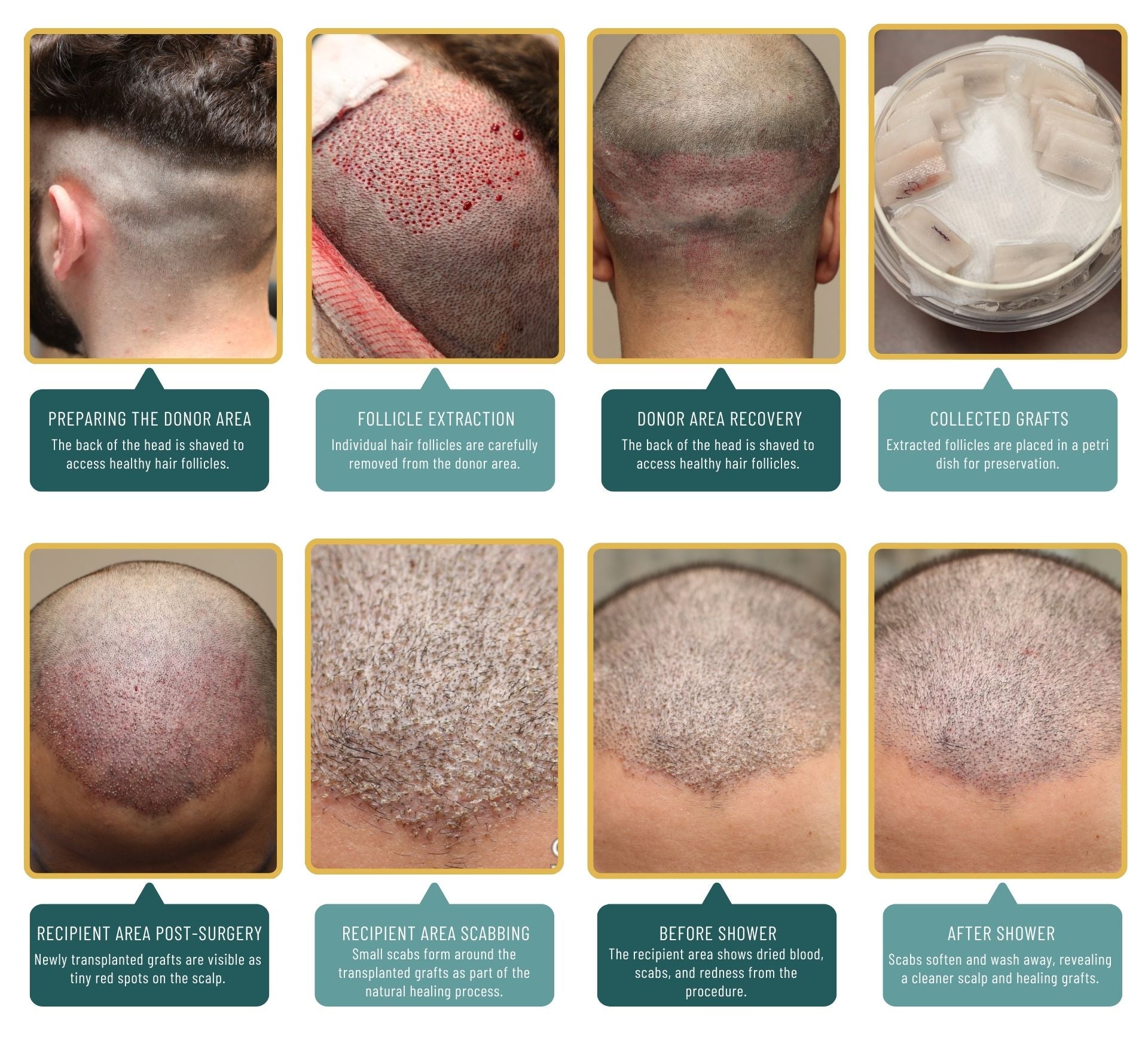
Post Hair Transplant Surgery
Surgical hair restoration patients are provided with a specific post-operative routine to follow for the first 10 days. After the procedure, if there is any discomfort related to the procedure it is normally treated with oral medications. Transplanted hair goes through the same resting and growing phases of your normal hair. The hairs of the transplanted grafts will begin to grow at approximately 4 months after your procedure and continue through months 10 – 12 post operation.
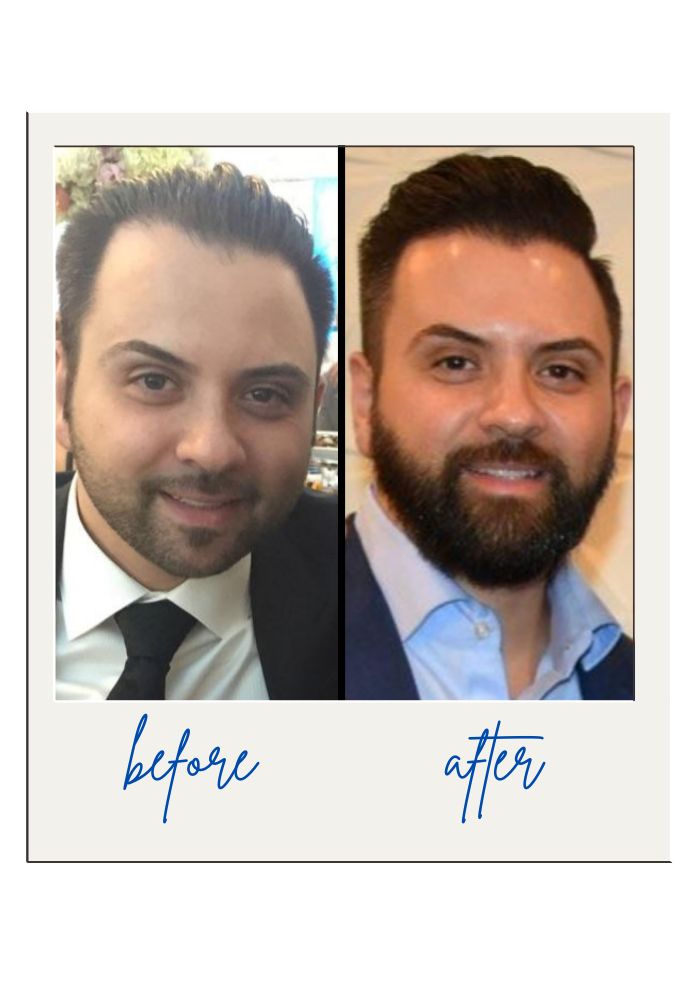

Real Patient Transformation
See the incredible results of a successful hair transplant. This patient restored natural hair density, achieving a fuller, more youthful look. With advanced techniques, the outcome is seamless and long-lasting.
Hairloss in Men
01. About Male Hairloss
Common male pattern baldness (MPB) accounts for more than 95% of male hair loss. By the age of thirty-five 2/3 of American men will experience some degree of appreciable hair loss, and by the age of fifty approximately 85% of men have significantly thinning hair. Approximately twenty five percent of men who suffer with male pattern baldness begin the painful process before they reach the age of twenty-one.
Male hair loss affects personal relationships as well as their professional life. It is not uncommon for men to change their career paths because of their hair loss.02. Causes of Male Hair Loss
Androgenic alopecia, or male pattern baldness (MPB), is the most common cause of hair loss in men, primarily due to genetics. It typically begins with a receding hairline and crown thinning, progressing to baldness across the scalp while often leaving a “horseshoe” pattern of hair.
DHT, a byproduct of testosterone, shrinks hair follicles over time, leading to hair loss. While the exact genetic process isn’t fully understood, suppressing DHT can slow or even stop hair loss if treated early.03. Diagnosis
Typical male pattern baldness is usually diagnosed based on the appearance and pattern of the hair loss, along with a detailed medical history, including questions about the prevalence of male hair loss in the family. An experienced medical hair loss expert should examine the scalp under magnification (preferably with a device called a densitometer), in order to assess the degree of miniaturization of the hair follicles. This assessment is very important when recommending the proper course of treatment.
Some advertised “clinics” might recommend a costly hair analysis or a scalp biopsy to properly diagnose your hair loss. The only reason to have a hair analysis is to assess the possibility of poison induced hair loss. A hair analysis may reveal substances such as arsenic or lead, however, hair loss caused by poising does not present itself in a typical male pattern. You should avoid these clinics and seek the advice of a physician who can properly examine you and help you treat your hair loss.

FAQs
What is a hair transplant, and how does it work?
A hair transplant is a surgical procedure that involves transferring hair follicles from one part of the scalp (the donor area) to areas experiencing hair loss or thinning (the recipient area). The two primary techniques used in hair transplantation are Follicular Unit Transplantation (FUT), which involves removing a strip of skin containing hair follicles, and Follicular Unit Extraction (FUE), which involves harvesting individual follicular units directly from the scalp. These transplanted follicles then continue to grow naturally in their new location, restoring hair density and improving overall appearance.
Who is a good candidate for a hair transplant?
Good candidates for a hair transplant are individuals experiencing hair loss or thinning hair who have sufficient donor hair on the scalp or other parts of the body. Ideal candidates have realistic expectations about the outcome of the procedure and are in good overall health. However, it's essential to undergo a consultation with a qualified provider to determine candidacy and discuss treatment options tailored to individual needs.
What can I expect during and after a hair transplant procedure?
During a hair transplant procedure, the patient is typically given local anesthesia to minimize discomfort, and the surgeon then carefully extracts or harvests donor hair follicles using either the FUT or FUE technique. These follicles are then implanted into the recipient area of the scalp, where they will establish blood supply and begin to grow new hair over time. The procedure can take several hours or longer, depending on the extent of hair loss and the number of follicles being transplanted. After the procedure, patients may experience some temporary discomfort, swelling, and scabbing in the donor and recipient areas, which typically subside within a few days to weeks. Hair growth will gradually occur over the following months, with full results typically visible within 6-12 months post-procedure. Regular follow-up appointments and post-operative care instructions provided by the surgeon are essential for optimal healing and outcomes.


